Introduction:Tossing and turning. Staring at the ceiling while your mind races. Sound familiar? In a world full of distractions, stress, and screens, falling asleep quickly
Read MoreIntroductionMain Idea: Something dramatic or mysterious to grab attention—such as, “Before your heart beats, before your eyes close forever, your nose may have sensed the
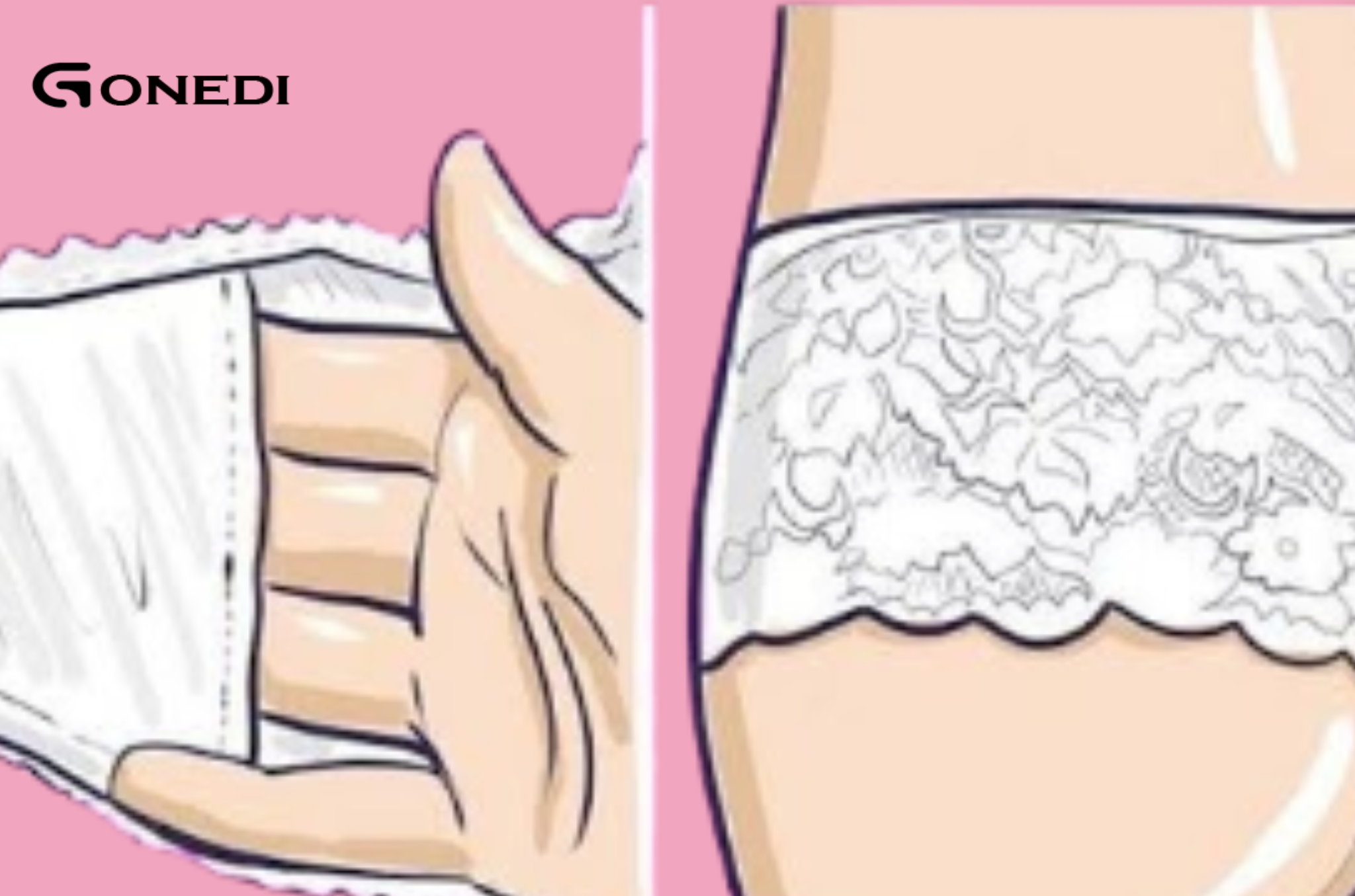
Read MoreIntroduction Have you ever noticed the tiny pocket sewn into your underwear and wondered what it’s for? You’re not alone! Many women have spotted this
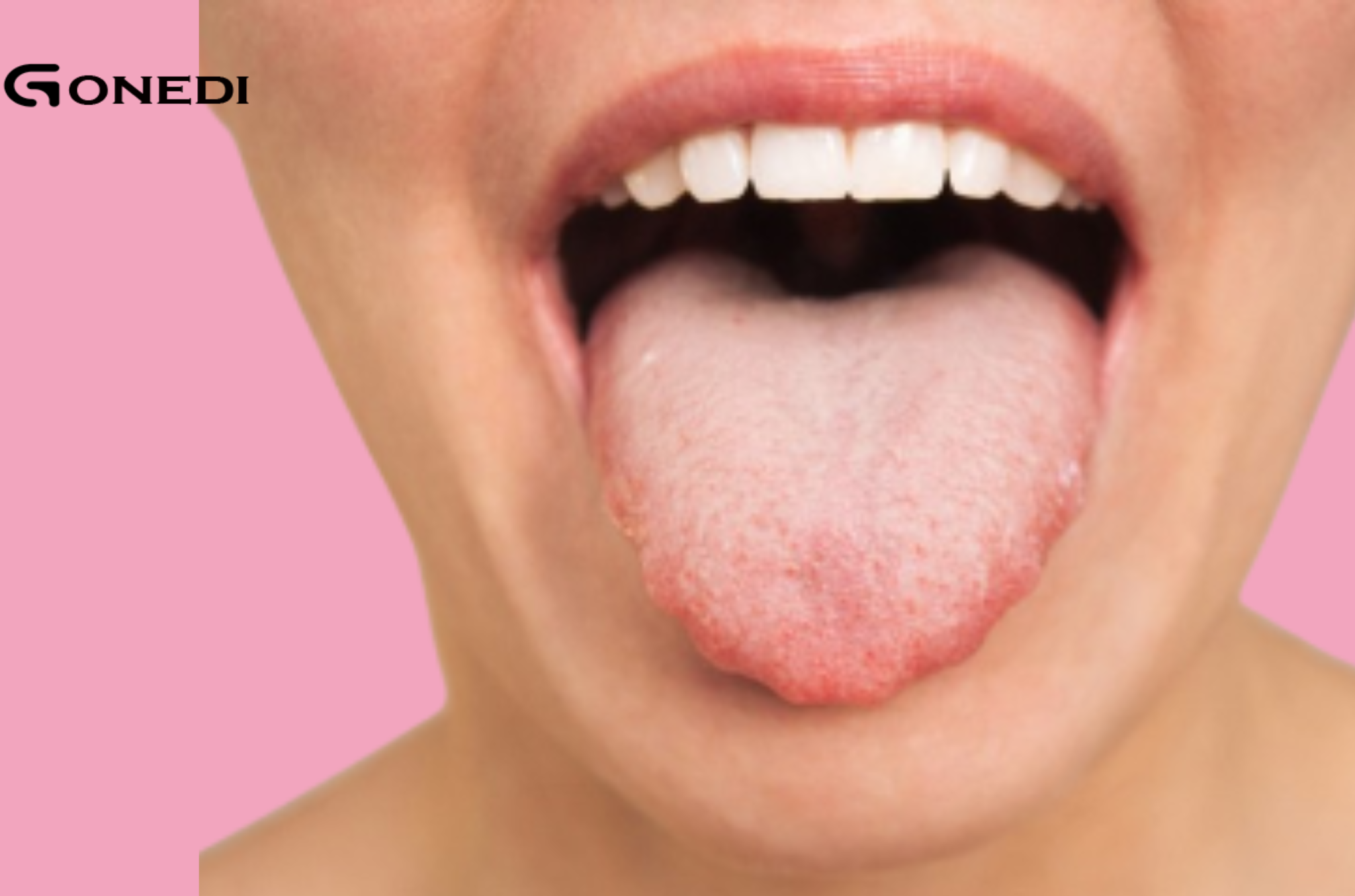
Read MoreIntroductionWhen we think of signs of illness, we often look for symptoms like fever or fatigue. But did you know that your tongue reveals a
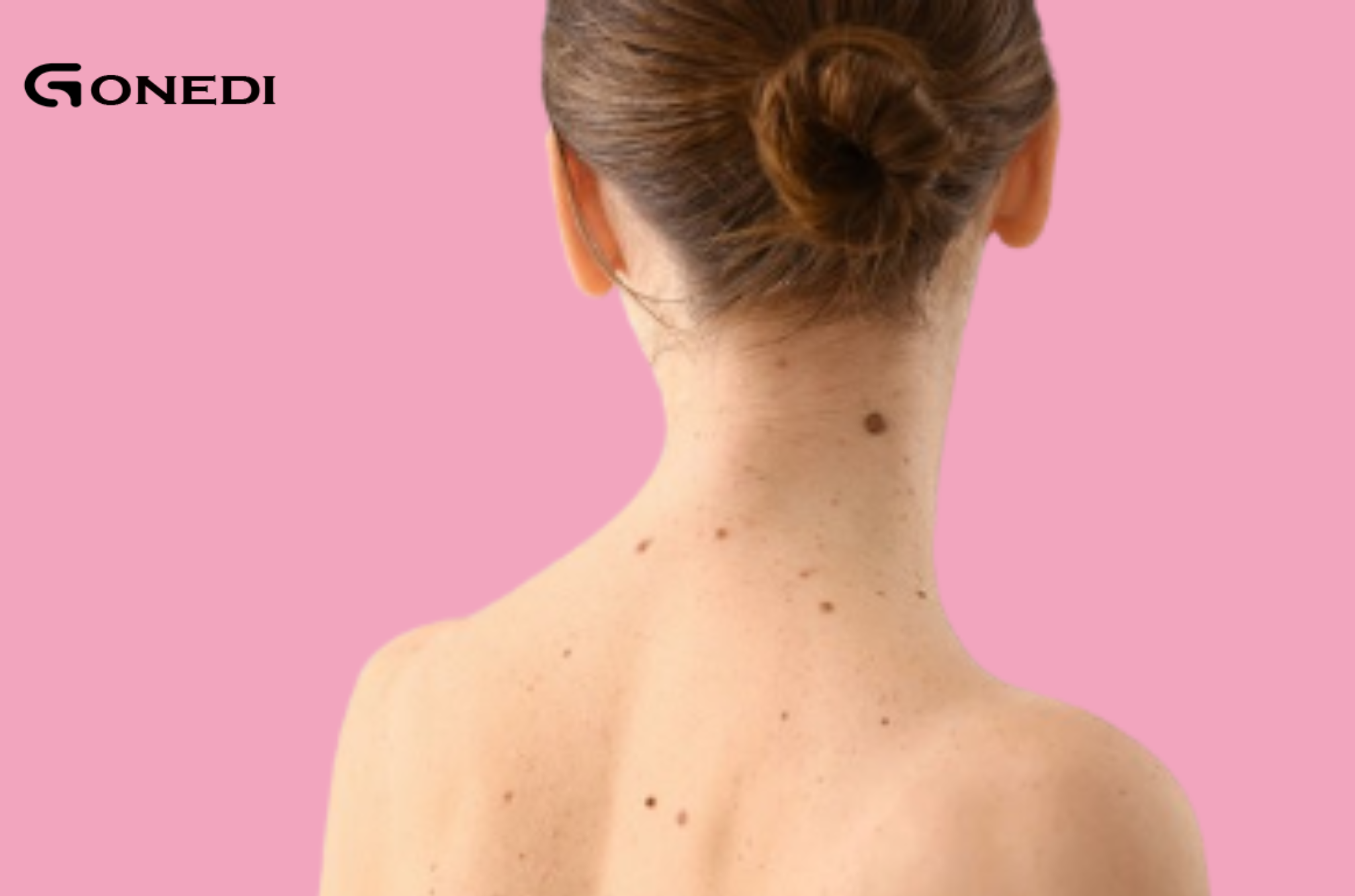
Read MoreIntroductionMoles are common skin growths that affect most people, but not all are created equal. While most are harmless, some moles in specific locations on
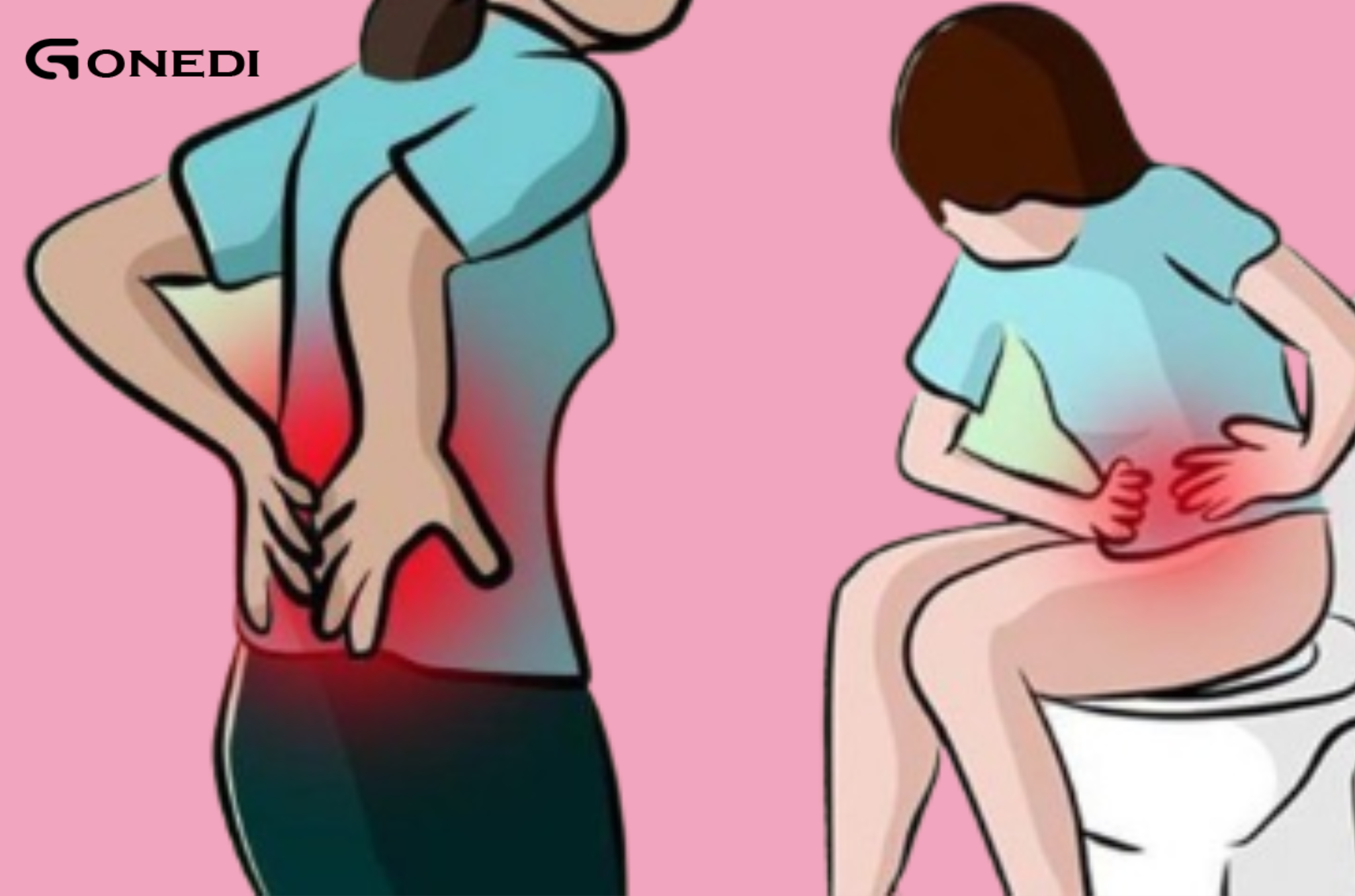
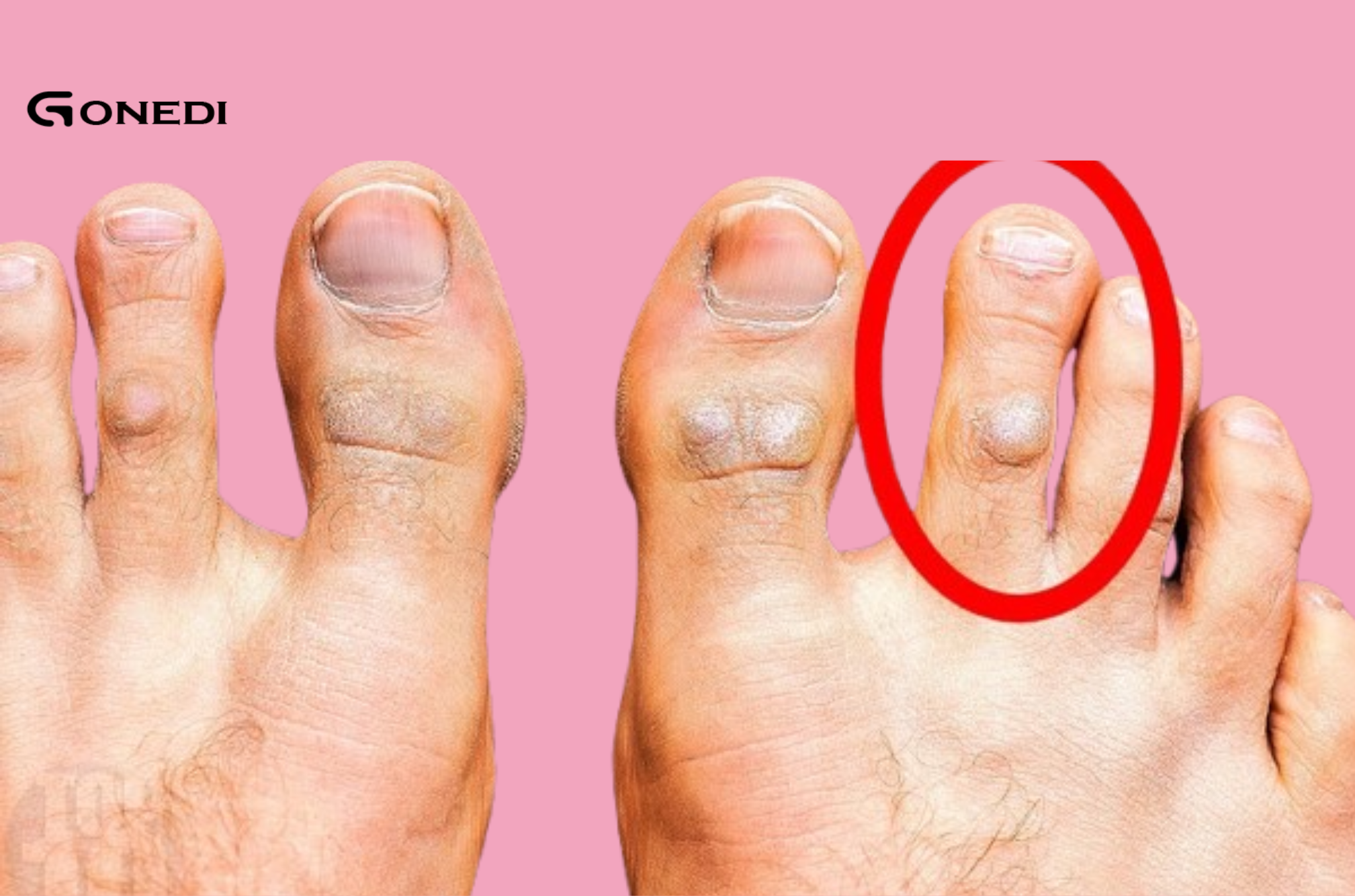
Read MoreColon cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, but it often goes undetected until its late stages because its symptoms can be
Read MoreBeauty comes in all shapes and sizes, and plus-size women have a unique charm that many men find irresistible. Society is slowly shifting toward body
Read MoreWhat it means: If you feel extremely tired even after a full night’s rest, it could be a sign of an underlying health problem. Chronic
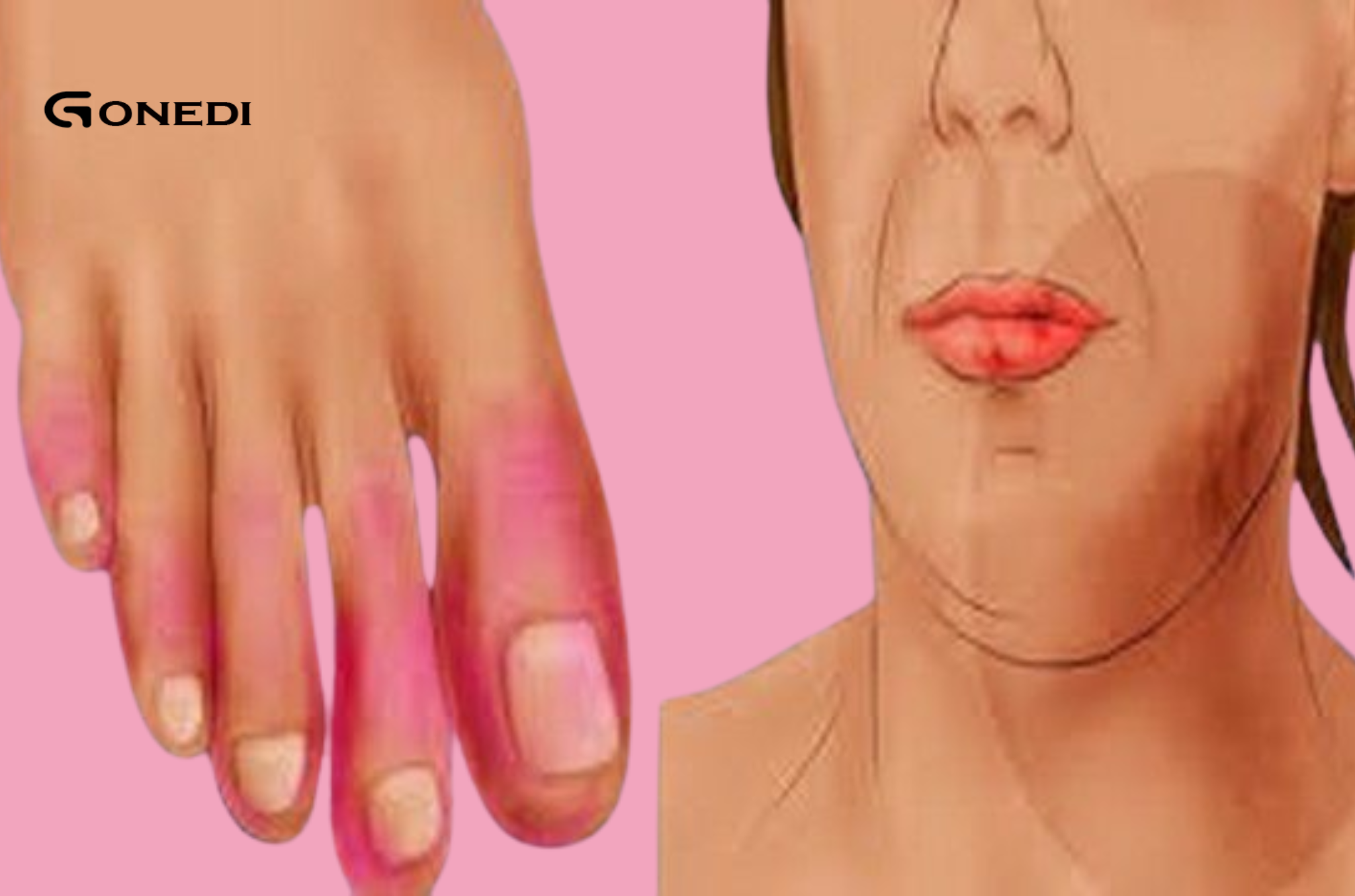
Read MoreLupus is a complex autoimmune disease that can manifest in a variety of ways. Recognizing the early signs can help ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
Read MoreMyelin sheath formation: Vitamin B12 is essential for the formation of myelin sheath, a protective covering around nerve fibers that helps nerve signals transmit efficiently.
Read More